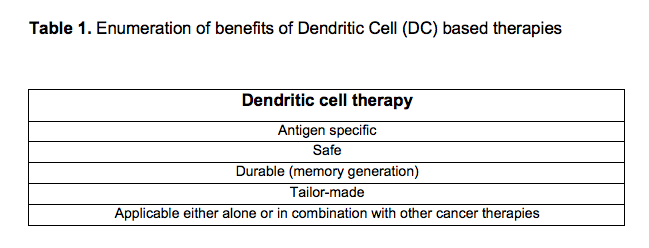
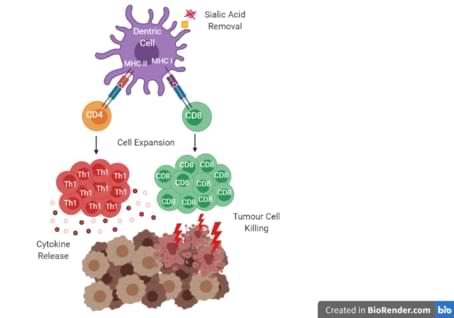
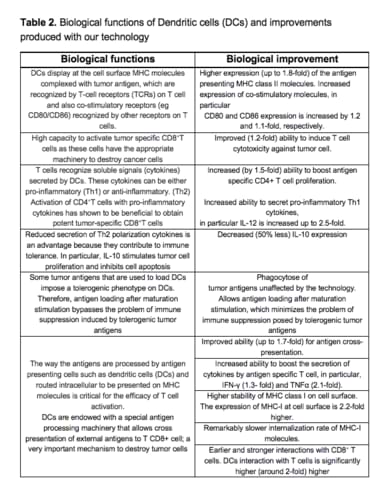
Dendritic cells (DCs) are key players in setting the immune system because they have an important role in antigen screening, uptake and presentation to T cells, ultimately triggering the adaptive response. Due to this prominent role, DCs are used as immunotherapies for different clinical indications, like cancer, autoimmune diseases or pathogen infection. However, DCs’ efficacy has shown to be limited to only a subset of patients, and it is urgent to boost their effectiveness and broaden their applicability.
Sialic acids are post-translational modifications of several proteins and its content change along with cell differentiation and activation, having important implications in cell ‘s functions. Sialic acids have a crucial role in immune modulation due to its recognition by lectin receptors, most of them with inhibitory endeavours. Moreover, changes in sialic acid content are associated with diseases as cancer, where oversialylation assumes to be a hallmark of cancer.